| Name | Calcium Gluconate |
| Classes |
Electrolyte and Mineral Nutritional Supplement |
| Diseases |
Hormonal Disorder Hypermagnesemia Hypocalcemia (Low Calcium) Hypoparathyroidism Osteoporosis (Brittle Bone) Tetanus |
Calcium Gluconate
Calcium gluconate is a mineral supplement and medication that is used to treat mineral overdoses of various kinds. It's commonly given as an intravenous infusion and injection.
Calcium gluconate is indicated for the following conditions-
- Antidote for severe hypermagnesemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypocalcemia/ Calcium deficiency
- Hypocalcemic tetany
The usual dosage of calcium gluconate is as follows-
- 500 mg - 2 grams for adults (5-20 mL)
- 200-500 mg for children (2-5 mL)
- Not more than 200 mg for infants (not more than 2 mL)
Calcium gluconate should be given intravenously, either as a direct injection or as an infusion. The dose is determined by the patient's specific requirements. Calcium gluconate can alternatively be given as a continuous infusion or as an intermittent infusion at a rate of no more than 200 mg/min.
Following intravenous infusion of calcium gluconate, patients may experience tingling sensations, a sense of oppression or heat waves, and a calcium or chalky taste.
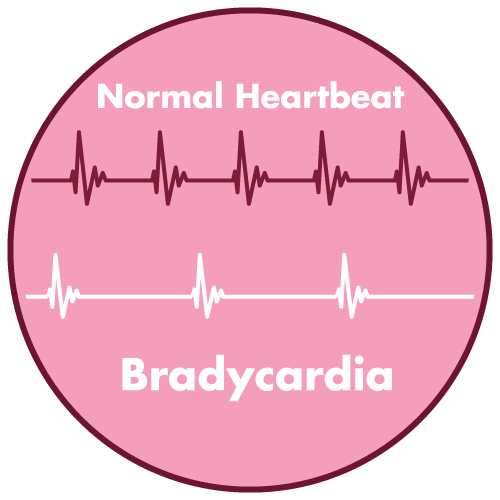
Vasodilation, hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, syncope, and cardiac arrest may occur after a rapid intravenous administration of calcium salts. Arrhythmias may occur if used in digitalized patients.
- To avoid the potentially harmful effects of rapid intravenous calcium gluconate delivery, the medicine should be administered slowly, such as 1.5 mL over one minute. Calcium gluconate should be given intravenously by a small needle into a big vein to avoid a rapid rise in serum calcium and calcium solution extravasation into the surrounding tissue, resulting in necrosis.
- Vasodilation, reduced blood pressure, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, syncope, and cardiac arrest are all possible side effects of a rapid calcium gluconate injection.
- Because of the risk of using calcium salts and digitalis-related medications at the same time, a digitalized patient should not receive an intravenous calcium compound injection unless the indications are apparent.
- When serum calcium levels are above normal, intravenous calcium delivery is not recommended.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to any component of the product.
There's no known contraindications of the medicine in terms of food and drinks.
Patients with ventricular fibrillation or hypercalcemia should avoid calcium salts.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English