| Name | Bisoprolol Hemifumarate |
| Classes |
Cardiovascular Agent Antihypertensive Beta-Adrenoceptor Blocker |
| Diseases |
Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
Bisoprolol Hemifumarate
Bisoprolol is a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoceptor blocking agent.
Bisoprolol hemifumarate is indicated for the following conditions-
- Adults: Individual dosage adjustments should be made. It is suggested that you begin with 5 mg each day. The normal dose is 10 mg once daily, with a maximum dose of 20 mg per day being recommended.
- Patients with kidney disease: The dose should not exceed 10 mg once daily in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 20 ml/min). This dosage may be divided in half in the future.
Commonly associated side effects of bisoprolol include-
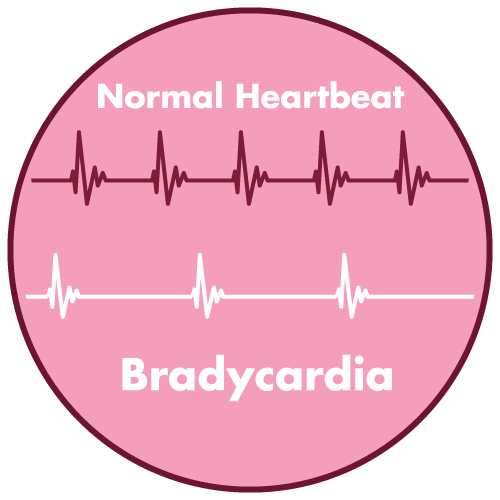
- Bradycardia
- Cold extremities
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, diarrhea)
- Fatigue/ asthenia
- Dizziness
- Bisoprolol should not be withdrawn abruptly.
- Due to unopposed alpha-receptor mediated coronary artery vasoconstriction, it may increase the number and duration of angina attacks in patients with Prinzmetal's angina.
- If given to individuals with first-degree heart block, caution should be maintained due to its unfavorable effect on conduction time.
- May obscure hypoglycemic symptoms, particularly tachycardia.
- It's possible that it'll disguise the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis.
- As a result of its pharmacological activity, it will lower heart rate. When a patient is being treated for a condition that could be caused by a sluggish heart rate and their pulse rate drops to less than 50–55 beats per minute at rest, the dose should be lowered.
Contraindication
Bisoprolol is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the drug or the excipients used in the medication.
Bisoprolol is contraindicated in the following health conditions-
- cardiogenic shock
- uncontrolled heart failure
- sick sinus syndrome (including sino-atrial block)
- second-or third-degree heart block
- untreated phaeochromocytoma
- metabolic acidosis
- bradycardia (< 45 bpm)
- hypotension
- severe peripheral arterial circulatory disturbances
 Bangla
Bangla English
English