| Name | Azelaic Acid |
| Classes |
Dermatological/Topical Agent Topical Antiinfective Agent Antiacne Agent Antirosacea Agent |
| Diseases |
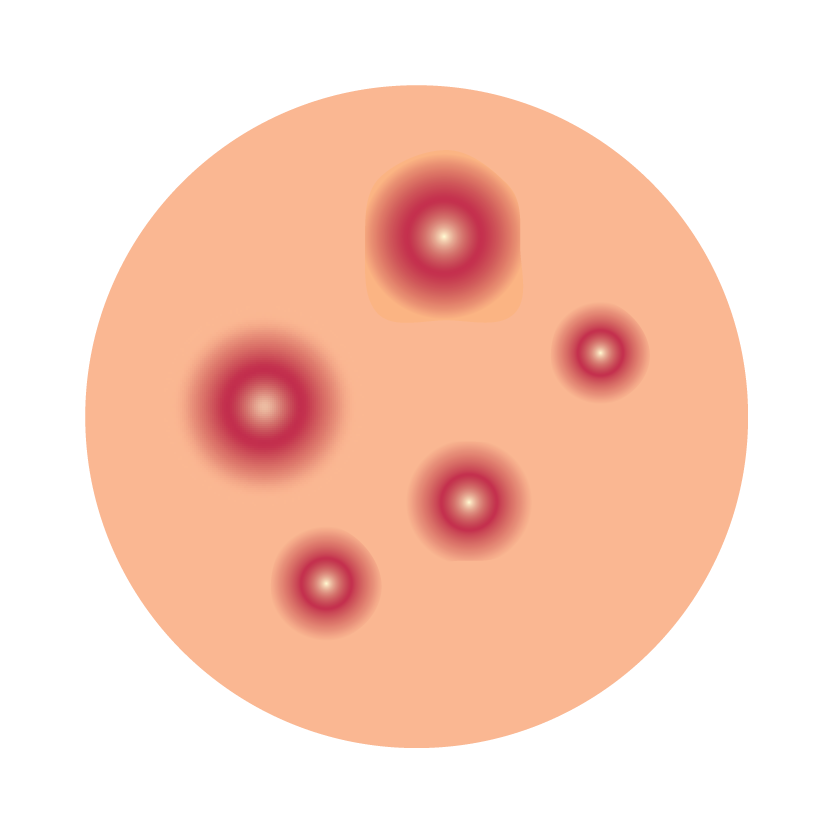
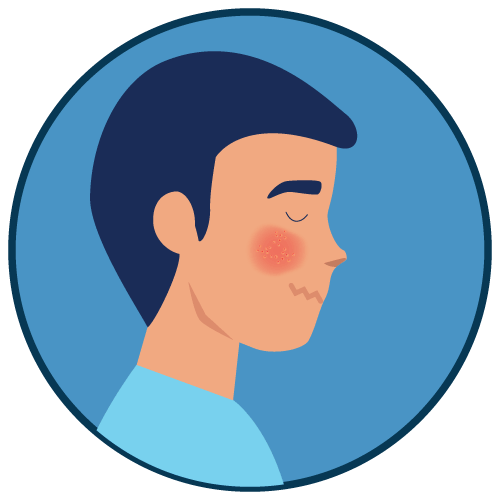
Acne Skin Disorder |
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. Its mechanism of action for the treatment of acne and rosacea is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by inhibiting the growth of Propionibacterium acnes, a bacteria associated with acne vulgaris. It also Decreases the formation of keratin, a protein that can contribute to the blockage of hair follicles. Azelaic acid also works by exerting anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Azelaic acid is available in topical cream, gel, and foam formulations.
- The recommended dose is to apply a thin layer of the medication to the affected area once or twice daily.
- Use only the amount needed to cover the affected area and avoid getting it in your eyes, mouth, and other mucous membranes.
- Common side effects include skin irritation, burning, stinging, itching, and redness.
- Serious side effects are rare but if you experience any severe or persistent side effects, stop using azelaic acid and seek medical attention immediately.
- Avoid exposure to sunlight or UV light while using azelaic acid as it may increase sensitivity to sunburn.
- If skin irritation occurs, discontinue use and consult your healthcare provider.
- Pregnancy and lactation: safety of azelaic acid in pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers has not been established. Consult your healthcare provider before using azelaic acid.
Contraindication
Do not use if you are hypersensitive to azelaic acid or any of the components of the formulation.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English