| Name | Atracurium Besylate |
| Classes |
Central Nervous System Agent Muscle Relaxant Skeletal Muscle Relaxant |
| Diseases |
Anesthesia Intubation Muscle String |
Atracurium Besylate
Atracurium Besylate belongs to the class of drugs known as non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents. It acts by competitively blocking the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, resulting in skeletal muscle relaxation and paralysis.
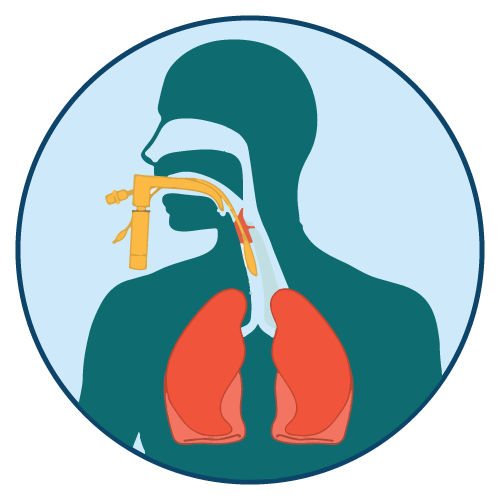
- Atracurium Besylate is indicated as an adjunct to general anesthesia to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation.
- It may also be used to facilitate endotracheal intubation and to improve surgical conditions during certain procedures.
Dosage by intravenous injection
- Atracurium besilate is administered by intravenous injection. The usual dose for adults ranges from 0.3 to 0.6 mg/kg of body weight (depending on the required duration of full block) and provides adequate relaxation for 15 to 35 minutes.
- Endotracheal intubation can usually be accomplished within 90 seconds from the intravenous injection of 0.5 to 0.6 mg/kg.
- Full block can be prolonged with supplementary doses of 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg as required. Successive supplementary dosing does not give rise to accumulation of neuromuscular blocking effect.
Adverse reactions to Atracurium Besylate may include:
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Flushing or erythema (redness of the skin)
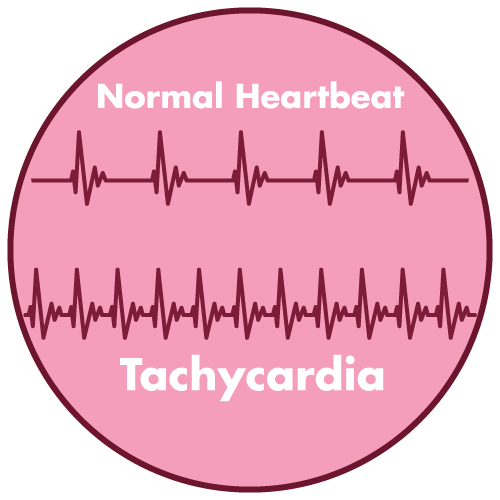
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat)
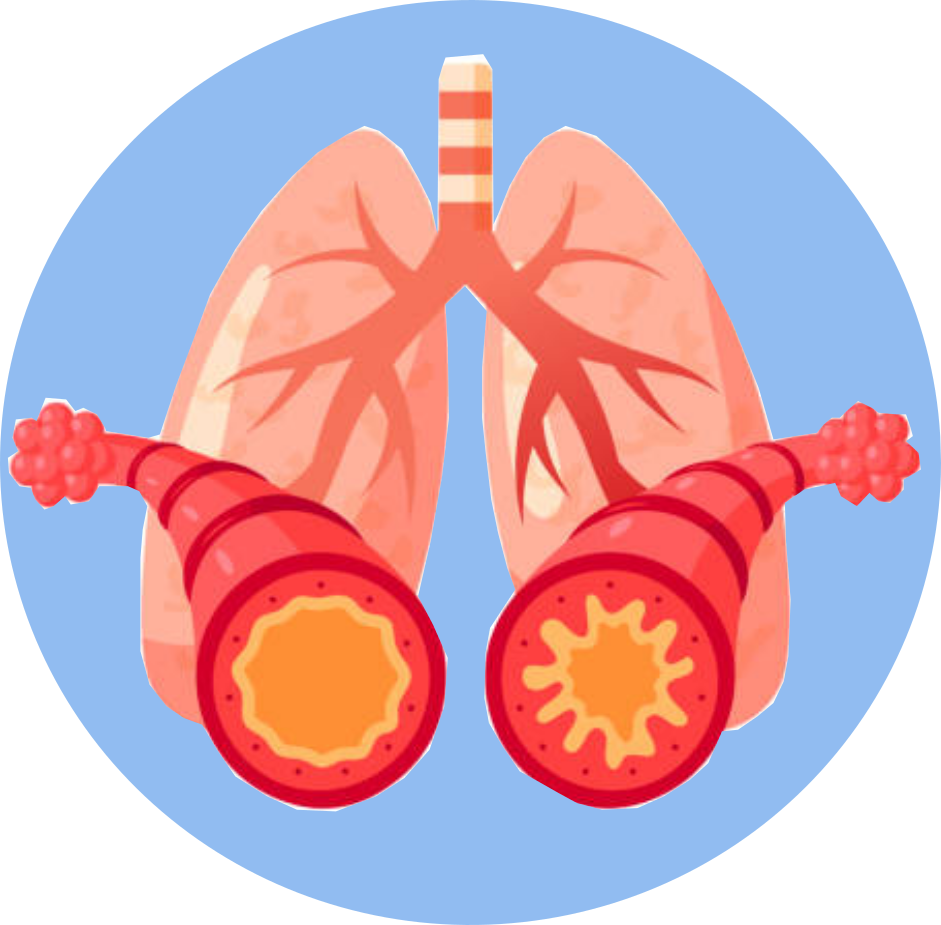
- Bronchospasm (constriction of the airways)
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash or itching
- Muscle weakness or prolonged paralysis
- Increased salivation or respiratory secretions
- Rarely, anaphylactic reactions (severe allergic reactions)
- Atracurium Besylate should only be administered by healthcare professionals experienced in the use of neuromuscular blocking agents and under appropriate monitoring conditions.
- It should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing neuromuscular disorders, electrolyte imbalances, or compromised cardiovascular or respiratory function.
- Adequate ventilation must be ensured during administration to prevent hypoxia and respiratory complications.
- Atracurium Besylate can potentiate the effects of other medications that cause neuromuscular blockade, such as inhalation anesthetics or other muscle relaxants. Careful dosage adjustments and monitoring are required in such cases.
- The use of Atracurium Besylate in patients with known or suspected allergies to the drug or its components should be avoided.
- Special caution should be exercised when administering Atracurium Besylate to patients with a history of allergic reactions to other neuromuscular blocking agents.
- Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients, pregnant women, and nursing mothers have not been fully established. Use in these populations should be based on careful risk-benefit assessment.
Contraindication
- Atracurium Besylate is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity or allergy to the drug or its component
- hypersensitivity to cisatracurium
None Known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English