| Name | Dorzolamide |
| Classes |
Dermatological/Topical Agent Ophthalmic Preparation Glaucoma Agent |
| Diseases |
Glaucoma Ophthalmic Disease Pressure inside Eye |
Dorzolamide
Dorzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor formulated for topical ophthalmic use. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye decreases aqueous humor secretion, presumably by slowing the formation of bicarbonate ions with subsequent reduction in sodium and fluid transport. The result is a reduction in intraocular pressure (IOP).
Dorzolamide is indicated for the-
- reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma
- ocular hypertension who are insufficiently responsive to beta-blockers
- The dose is one drop of Dorzolamide in the affected eye(s) two times daily.
- If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart
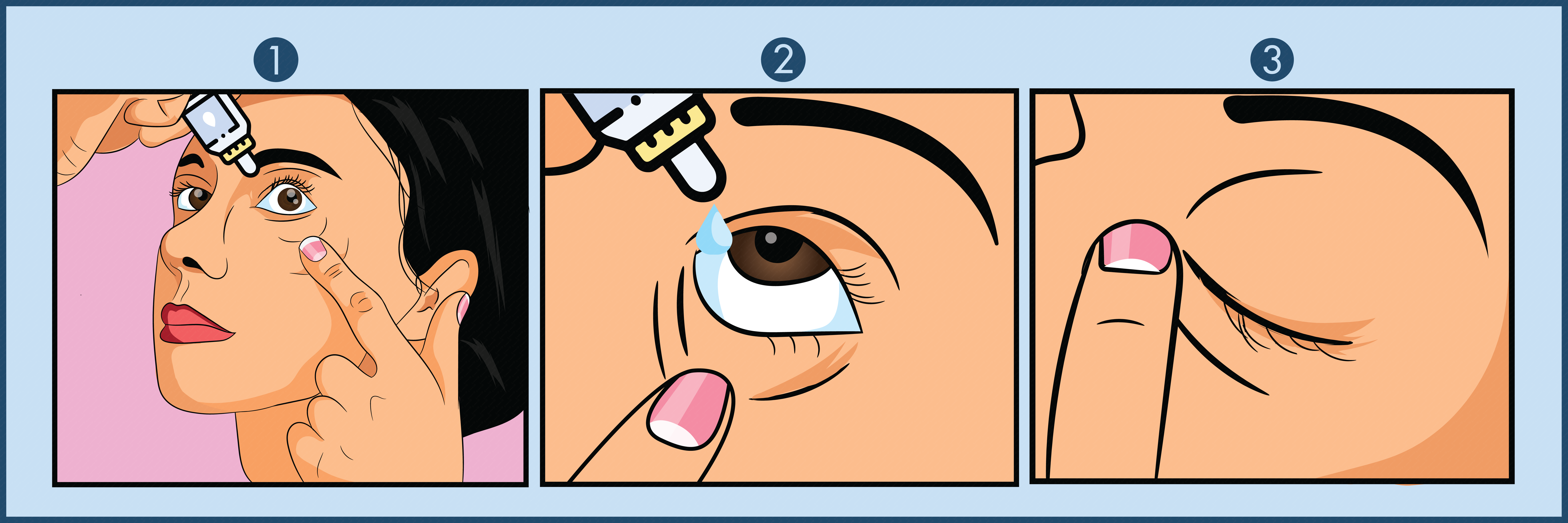
How to administer eye drops:
Commonly associated side effects include-
- eye burning
- eye stinging
- eye redness
- blurred vision
- eye tearing
- eye itching
- a bitter, sour, or unusual taste after putting in your eyedrops
- In addition to ocular hypotensive medications, individuals with acute angle-closure glaucoma require treatment approaches. In individuals with acute angle closure glaucoma, Dorzolamide has not been examined.
- Patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 30 mL/min) have not been investigated with Dorzolamide. Dorzolamide and its metabolite are primarily eliminated through the kidneys, hence Dorzolamide is not advised in these patients.
- Dorzolamide has not been tested in patients with hepatic impairment, so it should be used with caution in these individuals.
- Local ocular side effects, notably conjunctivitis and lid responses, have been described with continuous Dorzolamide treatment in clinical investigations. Many of these symptoms resembled an allergic reaction in appearance and course, and they all went away when the drugs were stopped. If such responses occur, Dorzolamide should be stopped and the patient assessed before restarting the medication.
- In patients receiving an oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and Dorzolamide, there is the possibility of an additive effect on the known systemic effects of carbonic anhydrase inhibition. It is not recommended to take Dorzolamide and oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors at the same time.
- There is an increased potential for developing corneal edema in patients with low endothelial cell counts. Precautions should be used when prescribing Dorzolamide to this group of patients.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English