| Name | Dexpanthanol |
| Classes |
Nutritional Supplement Vitamin |
| Diseases |
Dryness Skin Disorder Sore Nipple Wound |
Dexpanthanol
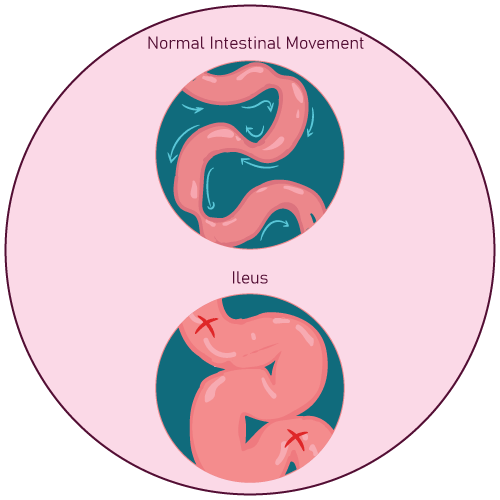
Dexpanthenol Injection is a sterile and nonpyrogenic solution that acts as a gastrointestinal stimulant. It is derived from pantothenic acid, which is a type of B complex vitamin. Pantothenic acid is involved in a variety of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that require the transfer of acetyl groups, and serves as a precursor of coenzyme A, a cofactor required for such reactions. In the final step of acetylcholine synthesis, choline acetylase transfers an acetyl group from acetylcoenzyme A to choline. Acetylcholine is a neurohumoral transmitter in the parasympathetic system, which helps maintain normal intestinal functions. A decrease in acetylcholine content can result in reduced peristalsis and even adynamic ileus in severe cases.
Dexpanthenol is indicated in the following conditions-
- Prophylactic use immediately after major abdominal surgery to minimize the possibility of paralytic ileus
- Intestinal atony causing abdominal distention
- postoperative or postpartum retention of flatus
- postoperative delay in resumption of intestinal motility
- paralytic ileus
- To prevent adynamic ileus after surgery, 250 mg (1 mL) or 500 mg (2 mL) of Dexpanthenol Injection can be given intramuscularly. This can be repeated every 2 hours, with subsequent doses every 6 hours until the risk of adynamic ileus has passed.
- To treat adynamic ileus, 500 mg (2 mL) of Dexpanthenol Injection can be given intramuscularly, with subsequent doses given every 2 hours and then every 6 hours as needed.
- For intravenous administration, 2 mL (500 mg) of Dexpanthenol Injection can be mixed with larger intravenous solutions like glucose or Lactated Ringer's and slowly infused.
- Before administration of parenteral drug products like Dexpanthenol Injection, the solution and container should be visually inspected for any discoloration or particulate matter.
- There have been rare instances of allergic reactions of unknown cause during the concomitant use of Dexpanthenol Injection with drugs such as antibiotics, narcotics and barbiturates.
- Administration of Dexpanthenol Injection directly into the vein is not advised.
- Dexpanthenol Injection should not be administered within one hour of succinylcholine.
- If any signs of a hypersensitivity reaction appear, Dexpanthenol Injection should be discontinued. If ileus is a secondary consequence of mechanical obstruction, primary attention should be directed to the obstruction.
- The management of adynamic ileus includes the correction of any fluid and electrolyte imbalance (especially hypokalemia), anemia and hypoproteinemia, treatment of infection, avoidance where possible of drugs which are known to decrease gastrointestinal motility and decompression of the gastrointestinal tract when considerably distended by nasogastric suction or use of a long intestinal tube.
Contraindication
There are no known contrandications of dexpanthenol.
None known.
None known.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English