| Name | Dexmedetomidine |
| Classes |
Central Nervous System Agent Sedative and Hypnotic |
| Diseases |
CNS Disorder Sleeping Disorder |
Dexmedetomidine
Dexmedetomidine is a selective alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. Dexmedetomidine acts on alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the central nervous system, leading to inhibition of norepinephrine release. This results in sedation, analgesia, and sympathetic nervous system suppression, providing a state of cooperative sedation in patients.
- To induce sedation in adult patients within the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), aiming for a sedation level no more profound than responding to verbal stimuli, as indicated by the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS) within the range of 0 to -3.
- To achieve sedation in adult patients who are not intubated before and/or during diagnostic or surgical procedures that necessitate a sedated state, specifically known as procedural or awake sedation.
Patients already intubated and sedated may switch to dexmedetomidine with an initial infusion rate of 0.7 micrograms/kg/h which may then be adjusted stepwise within the dose range of 0.2 to 1.4 micrograms/kg/h in order to achieve the desired level of sedation, depending on the patient's response. A lower starting infusion rate should be considered for frail patients. Dexmedetomidine is very potent and the infusion rate is given per hour. After dose adjustment, a new steady state sedation level may not be reached for up to one hour.
Adverse reactions of Dexmedetomidine are listed below-
- Hypotension
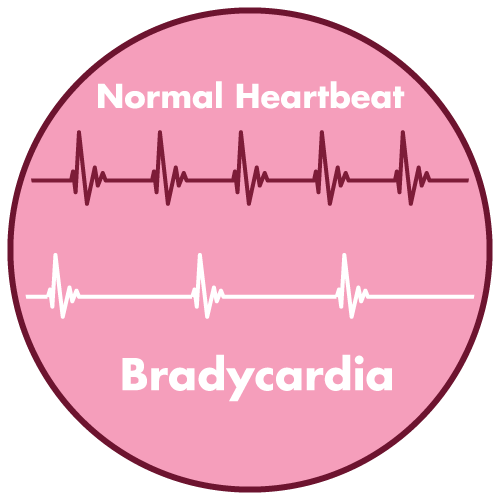
- Bradycardia
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
Hypotension and Bradycardia:
- Continuous monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate is essential during dexmedetomidine infusion.
- Dose adjustment or discontinuation may be necessary if severe hypotension or bradycardia occurs.
Respiratory Depression:
- Dexmedetomidine can cause respiratory depression, particularly when co-administered with other sedatives or opioids.
- Continuous monitoring of respiratory function is crucial.
Use in Elderly Patients:
- Elderly patients may be more susceptible to the hypotensive effects of dexmedetomidine.
- Careful titration and monitoring are recommended in this population.
Rebound Hypertension and Tachycardia:
- Abrupt discontinuation of dexmedetomidine may lead to rebound hypertension and tachycardia.
- Consider tapering the infusion rate gradually.
Contraindication
Contraindicated in patients with Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients.
None known.
Dexmedetomidine is contraindicated in the following conditions-
- Advanced heart block (grade 2 or 3) unless paced.
- Uncontrolled hypotension.
- Acute cerebrovascular conditions.
 Bangla
Bangla English
English